Technology
HEPA H13 Filter
Most Powerful: Medical Grade HEPA H13 Filter
History
The name HEPA stands for High Efficiency Particulate Air. The first idea behind the development of HEPA filter goes back to German soldiers during WW II, who were wearing gasmasks with inserted paper showing a remarkably high capture efficiency for chemical smoke. In the 1950 after a number of development stages the HEPA Filter was commercialised.
What is HEPA?
HEPA is a standard for filters as defined by the United States Department of Energy and in Europe by the European Standard EN 1822-1:2009. HEPA Filters are separated in several classes of efficiency. HEPA H13 and HEPA H14 are within the highest tier of HEPA and are considered medical grade Filters. ETS Air Disinfection Devices are equipped with HEPA H13 Filters which remove at least 99.95% of airborne particles 0.3 micrometers (μm) in diameter.
Caution: HEPA versus HEPA Type or HEPA Like
There are NO different Types of HEPA filters, as filters either meet of fail the norm in order to be called HEPA. The Term HEPA “Type”, HEPA “Style” or HEPA “Like” as advertised by many market participants is misleading, has no legal meaning and essentially is scientifically meaningless yet dangerous, since it insinuates safety and high level standards, which is not the case. The efficacy of such HEPA Type or HEPA Like filters do not meet the HEPA standards and may not have been tested.

Activated Carbon Filter
High Iodine Number: Activated Carbon Filter from ETS
Activated carbon Filters have special properties that allow to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odours, and other gaseous pollutants from the air. It accomplishes this in a way that is different from HEPA that only filter particle pollution from the air.
Why High Iodine Number?
The Iodine number is the most fundamental parameter used to characterize activated carbon performance. The Iodine number is a measure of the iodine adsorbed in the pores of the activated carbon and, as such, is an indication of the pore volume available in the activated carbon of interest. It is further a measure of efficiency level since the higher the iodine number the higher the degree of activation.
What will be filtered out?
Activated Carbon filters work through Adsorption, which is a distinct process where organic compounds in the air react chemically with the activated carbon, which causes them to stick to the filter. The more porous the activated carbon is, the more contaminants will be captured. Due to the high iodine number the ETS activated carbon filter has a high pore volume thus highly efficiently removing:
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) which are gaseous and hazardous compounds such as formaldehyde, benzene, or other hydrocarbons, which can be found in many products used to build and maintain residential and commercial buildings. Once these chemicals are in confined spaces, they are released or “off-gas” into the indoor air we breathe. They may or may not be able to be smelled, and smelling is not a good indicator of health risk.
- Odours

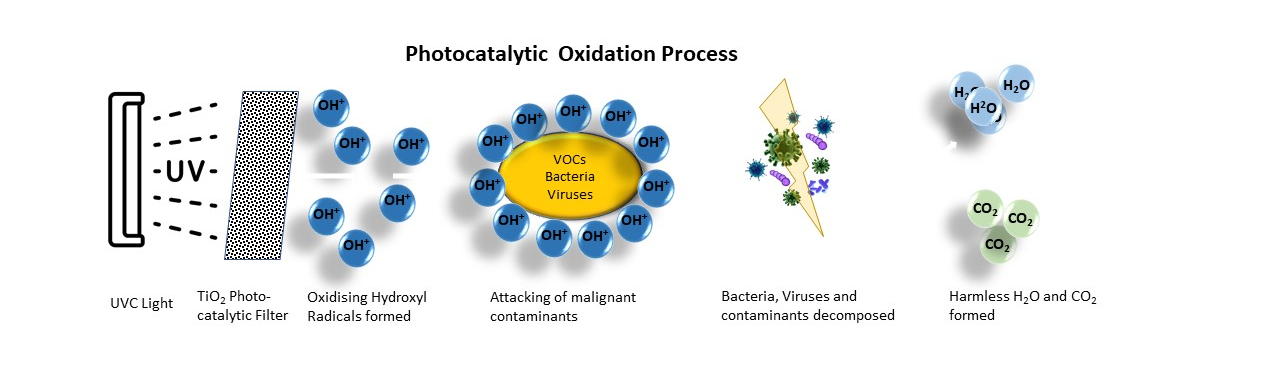
TiO2 Photocatalytic Oxidation Filter

Like in nature, but x fold more powerful:
TiO2 Photocatalytic Oxidation Filter from ETS
Photocatalytic Oxidation is a process that combines UVC irradiation with titanium dioxide (TiO2) as a photocatalyst which results in a reaction that changes malignant contaminants into water, carbon dioxide and detritus.
How does it work?
After passing the previous stages of filtration remaining contaminated air will be sucked through the honeycomb chambers of the TiO2 Photocatalytic Oxidation Filter on which backside a powerful UVC lamp triggers the promotion of electrons (e−) from the valence band to the conduction band leaving positive holes (h+) behind. Produced positive holes and free electrons diffuse to the semiconductor surface. The positive holes and electrons at the semiconductor/air interface, forming high reactive hydroxyl radicals and superoxide radicals, which subsequently initiate redox processes leading to the degradation/mineralization of adsorbed organic and inorganic compounds.
In other words Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC), bacteria and viruses will be attacked by free radicals and eliminated.
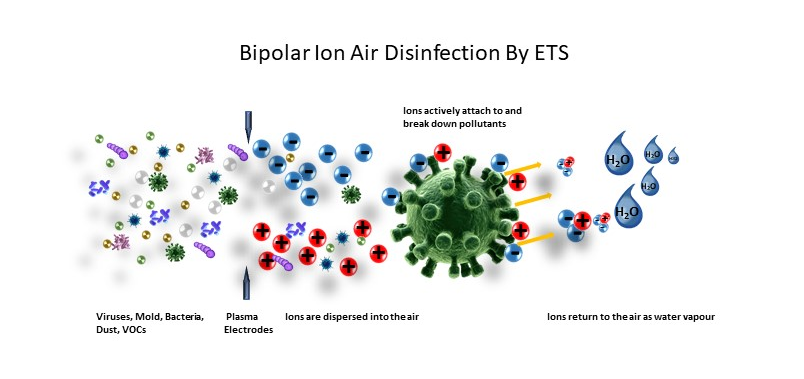
Bi-Polar Plasma
Nature shows us how it works: Bi-Polar Ionisation
In nature Ions are found in abundance. The highest concentration of bipolar ions are found around moving waters (ocean, waterfalls, thunderstorm etc.). That’s why the human body feels so energized and refreshed in these environments. In a confined room, though, the level of bipolar ions is the lowest, but usually concentration of harmful pollutants (VOCs, Germs, Viruses, Bacteria, etc.) are at their highest.
How does it work?
The bipolar ion generator in the ETS Air Disinfection System is located in the air outlet duct in which it creates bipolar ions through a high voltage plasma, generated between 2 electrodes, thus simulating the discharge of energy like in a thunderstorm. The charged ions or in other words activated negative Oxygen (O2- and positive Hydrogen (H+) molecules, carried by the air stream travel throughout the air space and attach themselves to airborne pollutants such as dust, mould, pollen and smoke, causing them to gain size and mass, enough that they drop to the floor, or return to the filter, making them easily cleaned from the air we breathe. Moreover, bipolar ions initiate an oxidation process, which chemically alters the odour molecules (VOCs) and germs. New harmless substances are formed. Activated oxygen damages the cell structure of mould spores as well as bacteria and viruses, so that they become inactive.